Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): Definition, Types, Classification & Working

An Internal Combustion Engine, or ICE as it is commonly called, is a heat engine in which fuel combustion occurs with the aid of an oxidizer. This process takes place in a confined space known as a combustion chamber. An internal combustion engine (ICE) is the traditional form of engine used in the majority of vehicles. Essentially, in an internal combustion engine (ICE), direct force is applied to engine components due to the high-pressure and high-temperature gases. Hence, this engine works by converting chemical energy into mechanical work.
What is Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)
An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a traditional engine in which the process of combustion of gases takes place. Air serves as an oxidizer in the combustion chamber, facilitating the efficient operation of the fluid flow circuit. A direct force is applied to the components of an internal combustion engine by the expansion of high-temperature, high-pressure gases.
The vehicles and machines that power our world have a heart and soul known as the internal combustion engine (ICE). When the combustion is intermittent in any engine having two and four-stroke pistons, that engine is known as an internal combustion engine.
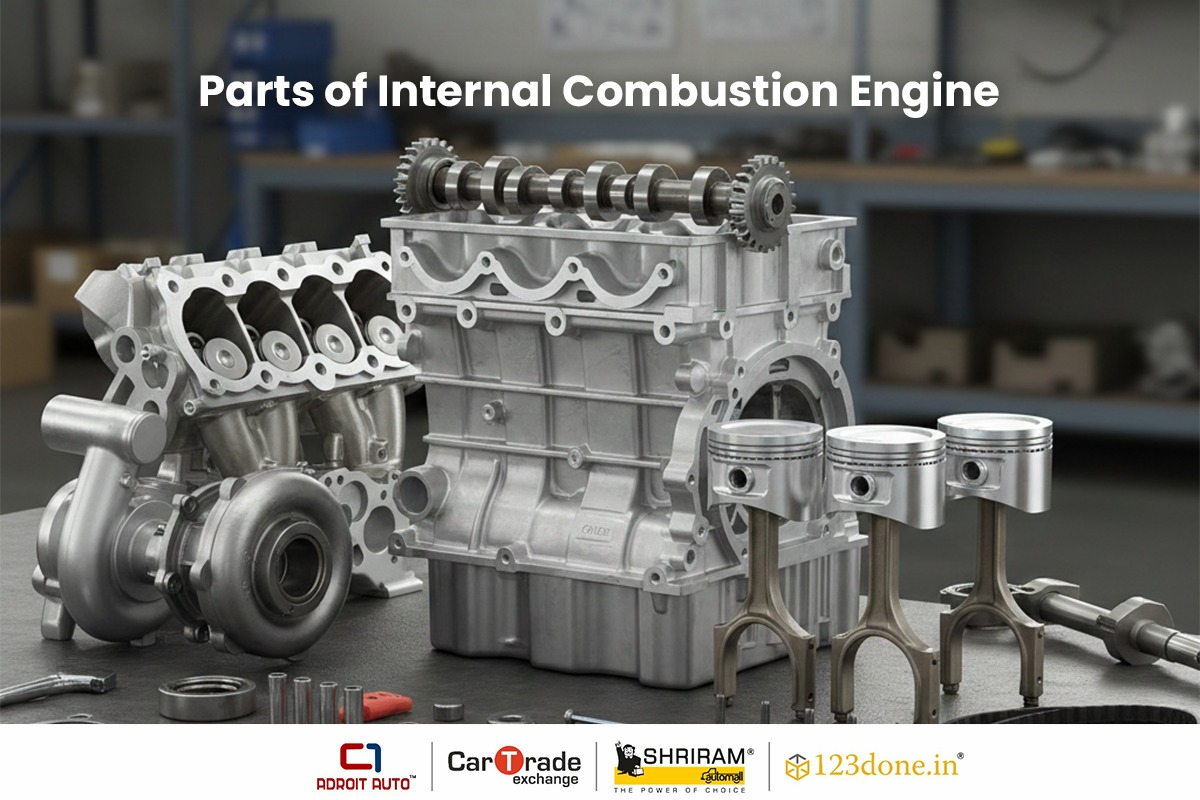
If you take a look at an internal combustion engine, it includes a piston, cylinder, crankshaft, fuel injector, camshaft, valves, and, in petrol cars, a spark plug. A cycle is performed by the working of these components, which is known as the Otto cycle for petrol engines and the Diesel cycle for diesel engines.
Classification & Types of Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)
Depending on certain functions or parts of the internal combustion engine, it is divided into several types. Based on the ignition method, strokes, fuel type, design, etc, the internal combustion engine (ICE) is classified into several types. Let us look at them closely with the help of a table:
|
CLASSIFICATION BASIS |
ENGINE TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
|
Ignition System |
Spark Ignition (SI Engine) |
Operates using a spark plug to ignite a precisely mixed air-fuel charge. Commonly found in petrol or gasoline vehicles, these engines are known for smooth acceleration and quieter performance. |
|
|
Compression Ignition (CI Engine) |
Relies on high compression to heat air inside the cylinder, causing diesel fuel to ignite automatically. Widely used in commercial vehicles due to better fuel efficiency and higher torque output. |
|
Operating Cycle (Strokes) |
Four-Stroke Engine |
Completes one power cycle in four piston movements: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. This design offers better fuel economy, lower emissions, and longer engine life. |
|
|
Two-Stroke Engine |
Produces power in just two piston strokes, making the engine lighter and mechanically simpler. Often used in small machines, though it consumes more fuel and emits higher pollutants. |
|
|
Six-Stroke Engine |
An advanced engine concept that adds extra strokes to improve thermal efficiency and reduce heat loss. Mostly seen in experimental and research applications. |
|
Fuel Type |
Petrol Engine |
Uses gasoline as fuel and is typically preferred for passenger cars due to its refined performance, lower noise levels, and quicker throttle response. |
|
|
Diesel Engine |
Runs on diesel fuel and is designed for durability and efficiency. Ideal for heavy-duty usage such as trucks, buses, and agricultural machinery. |
|
|
Gas-Powered Engine |
Uses alternative fuels like CNG, LPG, or biogas. These engines are more environmentally friendly and help reduce running costs and emissions. |
|
|
Biofuel / Multi-Fuel Engine |
Capable of operating on renewable or mixed fuels such as ethanol blends, biodiesel, or hydrogen combinations, supporting sustainability and fuel flexibility. |
|
Design & Mechanical Layout |
Inline Engine |
Cylinders are arranged in a straight line, offering a compact design, easier maintenance, and balanced performance for everyday vehicles. |
|
|
V-Type Engine |
Features cylinders placed in two angled banks forming a “V” shape. This layout allows higher power output while keeping engine length shorter. |
|
|
Horizontally Opposed (Boxer) Engine |
Cylinders lie flat and move outward from the centre, improving vehicle stability with a lower centre of gravity and reduced vibration. |
|
|
Radial Engine |
Cylinders are positioned around a central crankshaft in a circular pattern. Once popular in aircraft due to excellent cooling and reliability. |
|
|
Rotary (Wankel) Engine |
Uses a rotating triangular rotor instead of pistons. Known for compact size, high power-to-weight ratio, and smooth operation. |
|
Combustion Method |
Continuous Combustion Engine |
Burns fuel continuously rather than in cycles. Gas turbines and jet engines fall under this category and are mainly used in aviation and power generation. |
|
Cooling System |
Air-Cooled Engine |
Uses airflow to dissipate heat directly from engine components. Simple construction and lighter weight make it suitable for motorcycles and small engines. |
|
|
Water-Cooled Engine |
Circulates coolant through passages around the engine for effective temperature control, enhancing durability and consistent performance. |
|
Number of Cylinders |
Single-Cylinder Engine |
Contains one cylinder and is commonly used in small vehicles, generators, and agricultural tools due to low cost and easy maintenance. |
|
|
Multi-Cylinder Engine |
Employs multiple cylinders for smoother power delivery, higher speed capability, and improved overall engine performance. |
Working of Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)
Other than in vehicles, the internal combustion system (ICE) is also commonly used in generators and other industrial applications. In this type of engine, fuel and air is primarily mixed together, then combustion takes place where the fuel is burned inside the combustion chamber. A force is hence exerted on a piston, which converts the pressure into rotational motion with the help of a crankshaft. The vehicle works by the power generated through this process, and in the same way, other machinery works on the same principle.
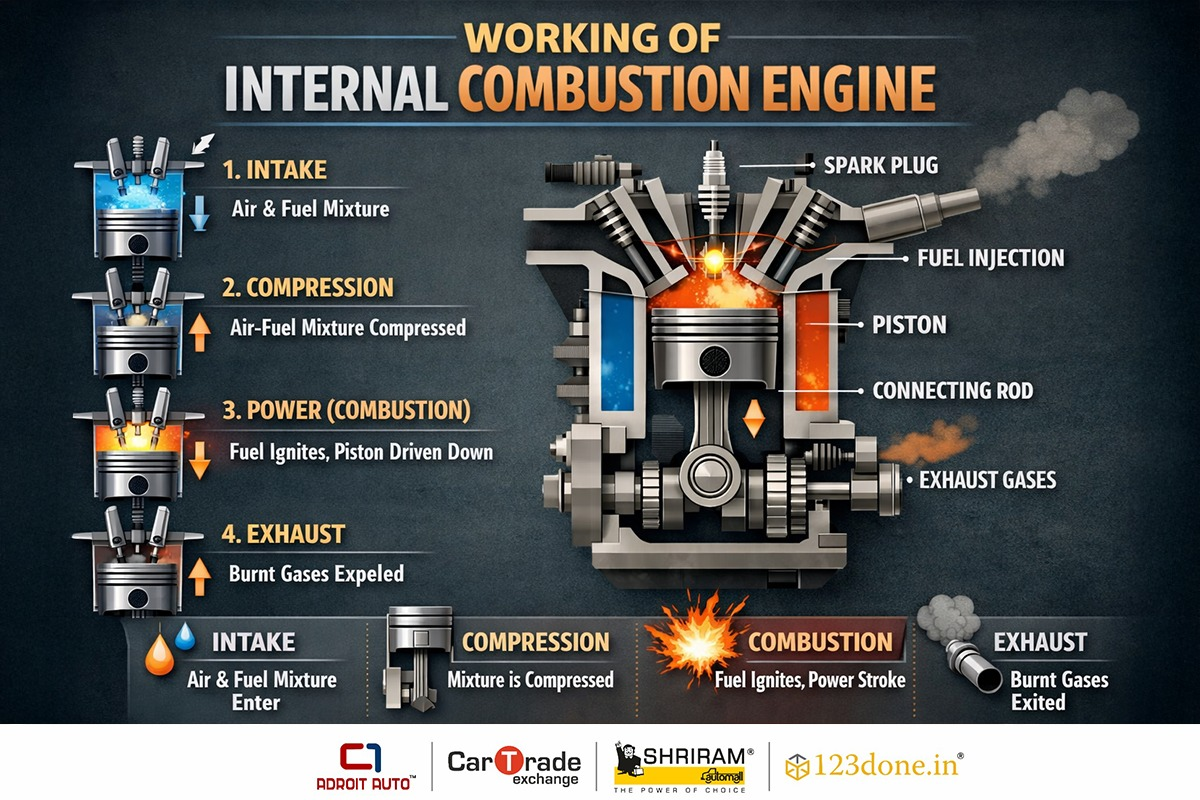
Depending on the fuel type, the internal combustion engine comes in different variations, like petrol engines or diesel engines. Both of these have their own combustion system, process, and characteristics.
Conclusion
The internal combustion engine (ICE) truly stands as a testament to the modern transportation and automotive industry. With a clear understanding of the definition of an internal combustion engine (ICE), its working, and different types based on classifications, one can get the idea as to why ICE is widely used. Internal combustion engines are gas-powered and fuel-powered to meet the specific performance and classification needs. New technologies like electric-powered vehicles are also emerging, but still, the internal combustion engine continues to be at the top, featuring better fuel efficiency and improved design.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an internal combustion engine in simple words?
An internal combustion engine is a type of engine where fuel burns inside the engine itself to produce power. This combustion creates pressure that moves engine parts and helps run vehicles and machines.
2. What are the main types of internal combustion engines?
The main types of internal combustion engines include petrol engines, diesel engines, gas-powered engines, and multi-fuel engines. They are also classified as two-stroke and four-stroke engines based on how they operate.
3. How does an internal combustion engine work?
An internal combustion engine works by mixing fuel and air inside a cylinder and igniting it. The explosion pushes a piston, which turns the crankshaft and converts this energy into motion that powers the vehicle or machine.
4. Is the internal combustion engine still relevant today?
Yes, the internal combustion engine is still widely used across cars, trucks, generators, and industrial equipment. While electric vehicles are growing, ICE technology continues to improve in efficiency and emission control, keeping it relevant for many applications.

 Download Our App
Download Our App



